Overview of AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS)#
AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS) is a fully managed container orchestration service that makes it easy to run, stop, and manage containerized applications. ECS has the following main features:
- High availability and scalability leveraging AWS infrastructure
- Support for Docker containers
- Integration with other AWS services
- Flexible scheduling options
Kong Gateway is a high-performance open-source API gateway that provides various features for managing, securing, and monitoring microservices. This article explains how to install Kong Gateway in an ECS environment. The overall installation flow is shown below.
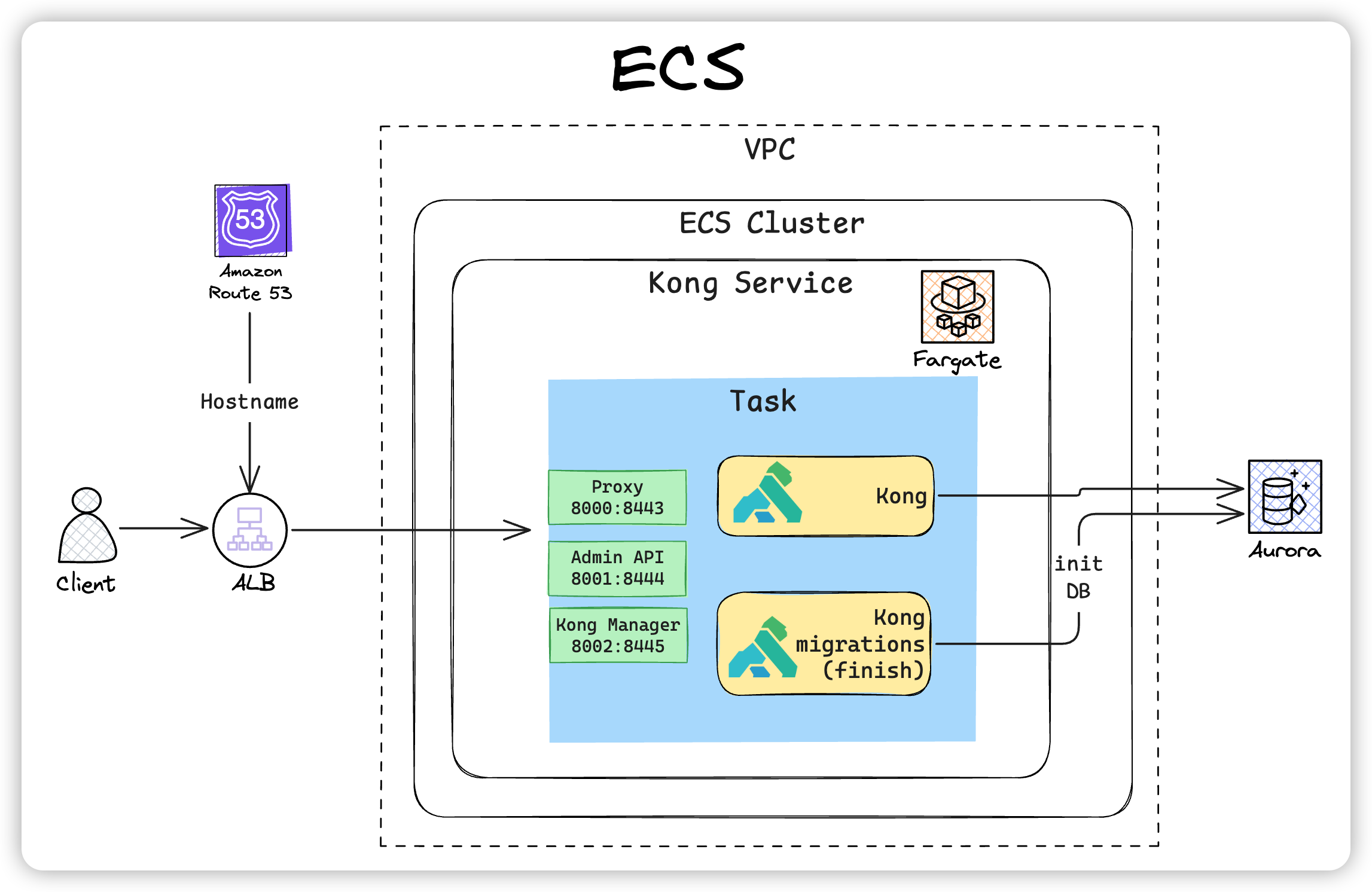
Preparing the Database#
For this deployment, we use an Aurora DB compatible with PostgreSQL. When creating the Aurora DB, you can specify the database name, so it’s easier to set it for Kong from the start.
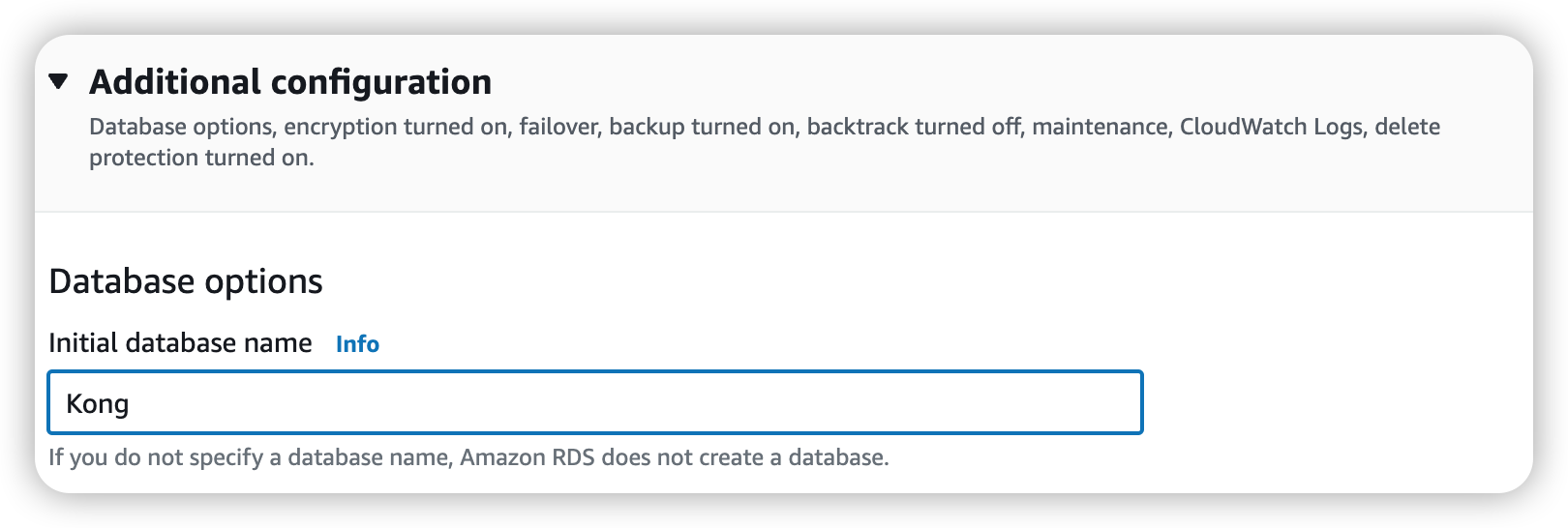
Preparing the ecs-cli Command#
Next, prepare the command. You can predefine access permissions and cluster information. Since we are creating a FARGATE type, set the default-launch-type to FARGATE.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| > ecs-cli configure profile \
--profile-name kong-profile \
--access-key xxxxxxxx \
--secret-key xxxxxxxx
INFO[0000] Saved ECS CLI profile configuration kong-profile.
> ecs-cli configure \
--cluster kong-ecs \
--region ap-northeast-1 \
--config-name kong-config \
--default-launch-type FARGATE
INFO[0000] Saved ECS CLI cluster configuration kong-config.
|
You can check these settings in the files under .ecs.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| > cat .ecs/config
version: v1
default: kong-config
clusters:
kong-config:
cluster: kong-ecs-demo
region: ap-northeast-1
default_launch_type: FARGATE
> cat .ecs/credentials
version: v1
default: kong-profile
ecs_profiles:
kong-profile:
aws_access_key_id: xxxxxxxxxxxx
aws_secret_access_key: xxxxxxxxxxx
|
Creating the ECS Cluster#
Based on the above settings, use ecs-cli to create the ECS cluster. Required resources such as VPCs and subnets are automatically generated.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| > ecs-cli up --capability-iam --cluster-config kong-config
INFO[0000] Created cluster cluster=kong-ecs-demo region=ap-northeast-1
INFO[0000] Waiting for your cluster resources to be created...
INFO[0001] Cloudformation stack status stackStatus=CREATE_IN_PROGRESS
VPC created: vpc-0c8bd4ff24a588273
Subnet created: subnet-08a35c8103b05b6a6
Subnet created: subnet-0211846377e4c3d29
Cluster creation succeeded.
|
If you want to use an existing VPC or subnet, specify them with the --vpc and --subnets options.
1
2
3
4
| > ecs-cli up --vpc vpc-xxxxxxxxxxx \
--subnets subnet-xxxxxxxxxxx,subnet-xxxxxxxxxxx,subnet-xxxxxxxxxxx\
--cluster-config kong-config \
--ecs-profile kong-profile
|
Once the VPC is set, check the security group ID next.
1
2
3
4
| aws ec2 describe-security-groups \
--filters Name=vpc-id,Values=vpc-xxxxxxxxxx | grep -i GroupId
"GroupId": "sg-yyyyyyyyyy",
"GroupId": "sg-yyyyyyyyyy",
|
After creating the ECS cluster, record the following resource IDs:
- VPC used
- Subnets
- Security groups
Preparing Task and Service Definition Files#
ECS task and service settings are defined in the following file. There are some points to note in this file:
- ecs_network_mode can only be set to awsvpc
- task_execution_role should be set appropriately
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| version: 1
task_definition:
ecs_network_mode: awsvpc
task_size:
cpu_limit: 256
mem_limit: 1024
task_execution_role: arn:aws:iam::xxxxxxxxxxxx:role/ecsTaskExecutionRole
services:
kong-migrations:
essential: false
logConfiguration :
logDriver: awslogs
options:
awslogs-group: kong
awslogs-region: ap-northeast-1
awslogs-stream-prefix: log-kong
kong:
hostname: kong
essential: true
depends_on:
- container_name: kong-migrations
condition: COMPLETE
logConfiguration :
logDriver: awslogs
options:
awslogs-group: kong
awslogs-region: ap-northeast-1
awslogs-stream-prefix: log-kong
run_params:
network_configuration:
awsvpc_configuration:
subnets:
- "subnet-08a35c8103b05b6a6"
- "subnet-0211846377e4c3d29"
security_groups:
- "sg-025b2859c18d70c2c"
assign_public_ip: ENABLED
|
Preparing the Container Definition File for the Service#
Define the startup conditions for the Kong Gateway container. Details of each parameter are omitted, but KONG_ADMIN_GUI_URL and KONG_ADMIN_GUI_API_URL should be set appropriately for your environment.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| version: "3"
services:
kong-migrations:
image: kong/kong-gateway:3.4.3.12
command: kong migrations bootstrap
environment:
- KONG_DATABASE=postgres
- KONG_PG_HOST=wenhan.cluster-cad2bwtkwmrs.ap-northeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com
- KONG_PG_USER=wenhan
- KONG_PG_PASSWORD=kongkong
- KONG_PASSWORD=kong
logging:
driver: awslogs
options:
awslogs-group: kong
awslogs-region: ap-northeast-1
awslogs-stream-prefix: log-kong-init
kong:
image: kong/kong-gateway:3.4.3.12
ports:
- 8000:8000
- 8001:8001
- 8002:8002
- 8443:8443
- 8444:8444
- 8445:8445
command: "kong start"
environment:
- KONG_ADMIN_GUI_URL=http://wenhan-manager.service-connectivity.com:8002
- KONG_ADMIN_GUI_API_URL=http://wenhan-admin.service-connectivity.com:8001
- KONG_DATABASE=postgres
- KONG_PG_HOST=wenhan.cluster-cad2bwtkwmrs.ap-northeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com
- KONG_PG_USER=wenhan
- KONG_PG_PASSWORD=kongkong
- KONG_PROXY_ACCESS_LOG=/dev/stdout
- KONG_ADMIN_ACCESS_LOG=/dev/stdout
- KONG_PROXY_ERROR_LOG=/dev/stderr
- KONG_ADMIN_ERROR_LOG=/dev/stderr
- KONG_PROXY_LISTEN=0.0.0.0:8000, 0.0.0.0:8443 ssl
- KONG_ADMIN_LISTEN=0.0.0.0:8001, 0.0.0.0:8444 ssl
- KONG_ADMIN_GUI_LISTEN=0.0.0.0:8002, 0.0.0.0:8445 ssl
- KONG_LOG_LEVEL=info
logging:
driver: awslogs
options:
awslogs-group: kong
awslogs-region: ap-northeast-1
awslogs-stream-prefix: log-kong
|
Starting Tasks and Services#
Use the compose up command to start the tasks and services. Specify the required files as parameters.
1
2
3
4
5
| ecs-cli compose \
--file docker-compose.yml \
--ecs-params ./ecs-params.yml \
--debug service up \
--create-log-groups
|
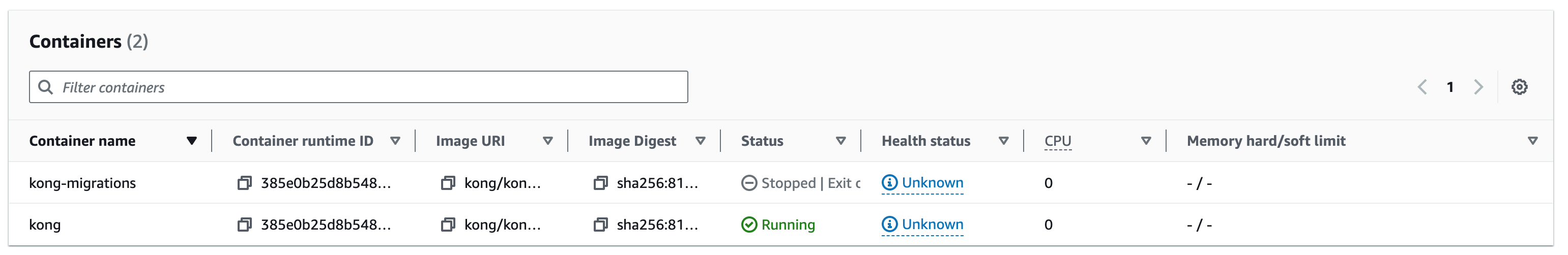
This will start two containers. The migrations container initializes the DB and will be in a Stopped state after processing. The other is the running Kong Gateway service.
From the task’s Networking, an external IP address is assigned, and you can access Kong’s service from this address.
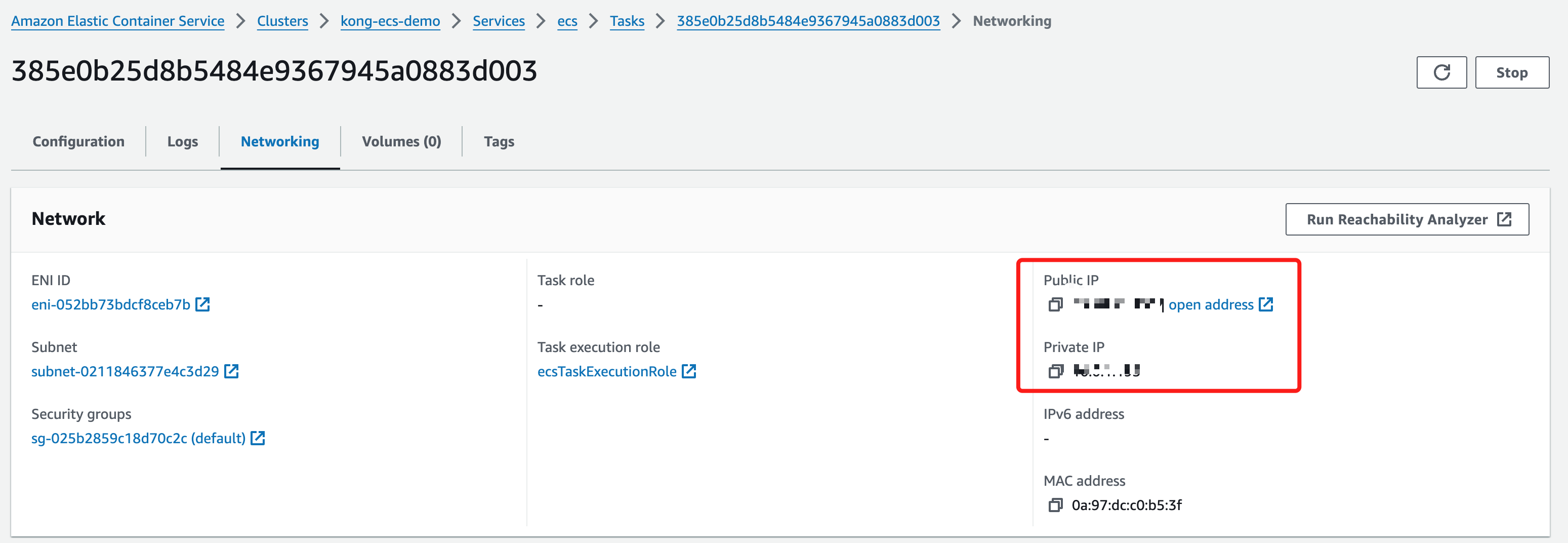
For example, you can access the Admin API at http://<IP address>:8001.
Stopping Tasks and Services#
1
2
3
4
| ecs-cli compose \
--file docker-compose.yml \
--ecs-params ./ecs-params.yml \
--debug service down
|
Postscript#
Remaining tasks:
- Create a Target Group pointing to this IP address and create an ALB
- Create a DNS entry from Route 53
Actually, the above tasks can be further automated using Terraform or CloudFormation, but that’s TBD.



