Security in API communication is extremely important for maintaining system reliability. This article provides a detailed explanation of how to configure mTLS (Mutual TLS) using Kong API Gateway. In particular, it covers how to set up mTLS for the two communication paths: “Client -> Kong” and “Kong -> Upstream API”.
Basics of mTLS
mTLS is an extension of TLS (Transport Layer Security) in which both sides of the communication (client and server) authenticate each other using certificates. While regular TLS only authenticates the server, mTLS adds the following processes:
- Server authentication: The client verifies that the server has a trusted certificate.
- Client authentication: The server verifies that the client has a trusted certificate.
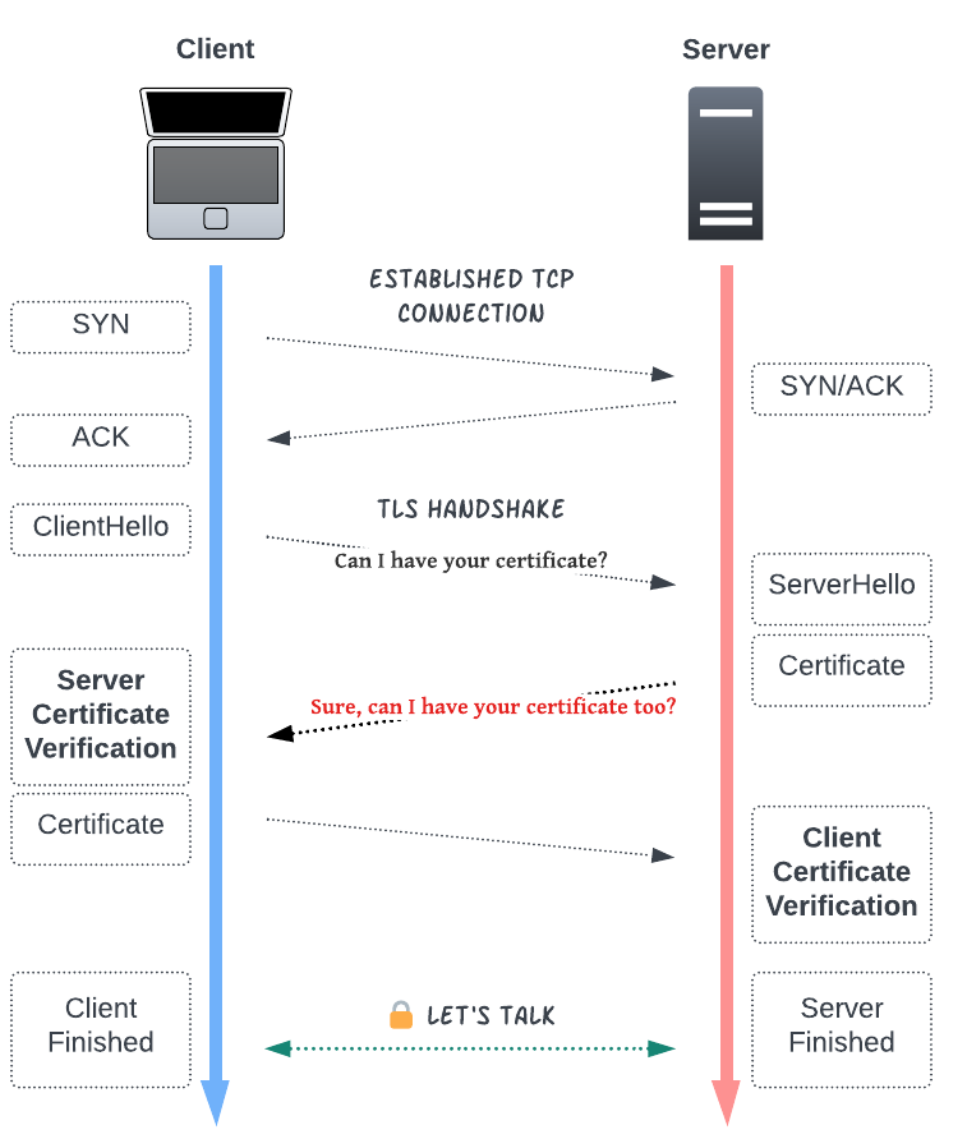
This bidirectional authentication enables more secure communication.
Achieving mTLS Communication with Kong API Gateway
With Kong API Gateway, you can easily implement mTLS on the following two communication paths:
- Client → Kong API Gateway
- Kong API Gateway → Upstream API

mTLS Settings for Client->Kong
To implement mTLS for communication from the client to Kong API Gateway, use Kong’s “mTLS Plugin”. The steps are as follows:
- The administrator sets the CA certificate for client authentication in Kong
- The client presents its own certificate to Kong when making a request
- Kong verifies the client certificate and allows secure communication
Register the CA Certificate
Register the CA certificate in Kong to verify the client’s certificate
| |
Enable the mTLS Plugin
Enable the mTLS plugin using the ca_certificate created above. Here, it is specified at the global scope.
| |
At this point, if you try to access without a client certificate, you should get an HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized error.
Access with a Client Certificate
Since mTLS means mutual TLS authentication, you must use the HTTPS protocol when accessing. If Kong’s TLS certificate is self-signed, you may need to add the -k flag to skip certificate verification.
| |
| |
mTLS Settings for Kong->Upstream API
When Kong accesses the API, the Upstream API requires a client certificate. Therefore, you need to register a client certificate on the Kong side. There are two ways to register: globally for Kong, or per Service.
Register Globally for Kong
Add the following three parameters to the configuration file. When Kong sends a request to the API, it will also send the client certificate.
| |
Register Per Service
When creating a Service, you can add a client certificate with client_certificate.
The priority is: per Service > global. If both are set, the Service setting takes precedence.
Conclusion
By properly configuring mTLS, you can greatly enhance the security of API communication. This article introduced how to set up mTLS for the two communication paths: “Client -> Kong” and “Kong -> Upstream API”.
To ensure secure API communication, keep the following points in mind:
- Properly manage the CA certificate for client authentication
- Correctly configure the client certificate between Kong and the Upstream API
- Use global or per-Service settings as appropriate
Refer to the diagrams and try introducing mTLS in your own environment.